What Is Ketamine Made Of? A Complete Guide to the Chemistry, Creation, and Clinical Magic Behind This Powerful Molecule
You’ve probably heard of ketamine as a “horse tranquilizer,” a party drug, or even a revolutionary mental health treatment—but what is ketamine made of, really?
Is it synthetic? Is it natural? What’s inside that mysterious vial doctors use for anesthesia or mental health infusions?
Buckle up, because we’re going to unpack everything—from atoms and molecules, to laboratory synthesis, to clinical-grade formulations. And don’t worry—no chemistry degree required! Whether you’re a curious patient, a health professional, or just fascinated by science, this guide is here to make ketamine’s complexity approachable, fascinating, and yes, even a little fun.
1. The Chemical Composition of Ketamine: It All Starts with the Molecule
Let’s get geeky (in a good way)!
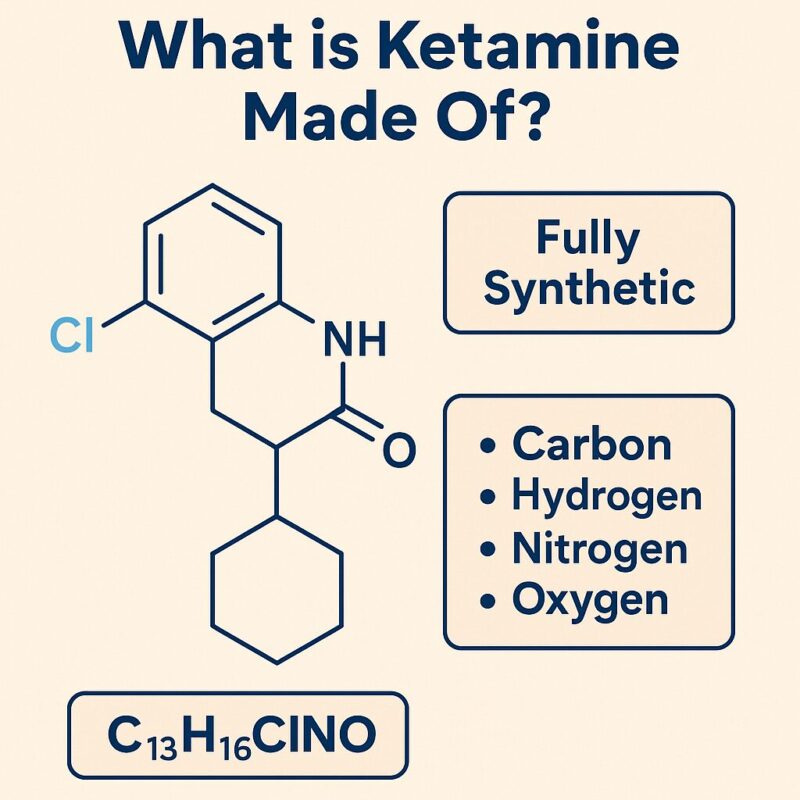
🧪 The Molecular Formula
The core molecular formula of ketamine is:
C₁₃H₁₆ClNO
That means it’s made up of:
- 13 carbon atoms
- 16 hydrogen atoms
- 1 chlorine atom
- 1 nitrogen atom
- 1 oxygen atom
And these aren’t just randomly tossed together. They’re arranged in a specific 3D configuration that gives ketamine its powerful effects—both as a dissociative anesthetic and a fast-acting antidepressant.
🌀 The Magic of Chirality: R- and S-Ketamine
Here’s where things get mind-bending (literally): ketamine is a chiral molecule. That means it exists in two mirror-image forms:
- S-ketamine (esketamine)
- R-ketamine (arketamine)
These are called enantiomers, and although their atoms are the same, their orientations are reversed—just like your left and right hands. This matters because S-ketamine binds more strongly to NMDA receptors and is used in the FDA-approved Spravato® nasal spray, while R-ketamine is being researched for longer-lasting antidepressant effects.
2. What Ketamine Is NOT Made Of: Busting a Few Myths
Before we get into how ketamine is actually made, let’s clear up a few common misconceptions:
- ❌ Not derived from plants – It’s fully synthetic.
- ❌ Not related to opioids – It has no chemical similarity to morphine or fentanyl.
- ❌ Not a psychedelic – It’s a dissociative anesthetic, though the experience may feel psychedelic.
That said, it can be life-changing—and life-saving—when used correctly.
3. How Is Ketamine Made? The Synthesis Process Explained
Here’s the million-dollar question: how do scientists create ketamine in the lab?
🧪 Raw Materials & Precursors
The production process generally involves:
- Cyclohexanone – a common industrial chemical
- Chlorobenzene – introduces the chlorine atom
- Methylamine or similar amine – adds the nitrogen group
These components go through several steps, including:
- Grignard Reaction – to build the core carbon structure.
- Amine Alkylation – to introduce the nitrogen.
- Ring Closure – to create the arylcyclohexylamine structure.
- Purification – distillation, crystallization, and drying to produce ketamine hydrochloride (a stable, water-soluble salt).
Sounds complex? It is! The end result: a white crystalline powder of ketamine HCl—the form you’ll find in IV bags, vials, or nasal sprays.
4. What Is Ketamine Made Of… In The Final Form?
Once the raw molecule is made, it’s turned into various medical-grade formulations:
💉 Ketamine Hydrochloride
This is the most common form used in clinics and hospitals. Why hydrochloride? Because:
- It’s water-soluble.
- It allows for precise dosing.
- It’s chemically stable over time.
This form is often:
- Injected (IV or IM)
- Infused in a clinical setting
- Used off-label for depression and pain management
👃 Esketamine (Spravato®) Nasal Spray
This formulation contains only the S-enantiomer and is FDA-approved for treatment-resistant depression. It includes:
- Esketamine hydrochloride
- Carrier solution (often water or saline with preservatives)
- Administered via nasal atomizer in clinics
👅 Sublingual & Oral Forms
Often prepared in compounding pharmacies. These typically combine:
- Racemic ketamine or pure enantiomer
- Flavorings, binders, and sometimes stabilizers for pH balance
5. What Makes Ketamine “Work”? The Pharmacological Composition
Ketamine is no ordinary anesthetic.
🧠 Mechanism of Action
It mainly works by blocking NMDA receptors, which:
- Reduces glutamate activity (a major excitatory neurotransmitter)
- Causes a dissociative, analgesic, and antidepressant effect
But that’s not all…
It also:
- Boosts BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor)—great for neuroplasticity!
- Enhances AMPA receptor activity
- Triggers the production of norketamine and hydroxynorketamine, which have antidepressant effects without the “trip”
How cool is that?!
6. From Molecule to Medicine: Manufacturing Standards Matter
Making ketamine isn’t just about tossing chemicals into a beaker.
🏭 Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Manufacturers must adhere to:
- GMP-certified facilities
- Batch testing for impurities
- Documentation for traceability
- Purity standards (often >99%)
🧪 Analytical Tools Used
- NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) – ensures molecular structure is correct
- HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) – confirms purity
- Mass Spectrometry – checks molecular weight and fragmentation
Every vial or nasal spray you see has gone through multiple layers of safety and efficacy testing.
7. Why “What Ketamine Is Made Of” Really Matters
Understanding what ketamine is made of helps clarify:
- Why racemic ketamine differs from esketamine
- Why IV infusions might feel stronger than oral forms
- Why some people tolerate it better than others
🧠 Therapeutic Effects Depend on Molecular Details
- Enantiomer composition affects potency and side effects
- Metabolites influence duration and tolerability
- Delivery format determines bioavailability
8. Is Ketamine Natural or Synthetic? (Spoiler: Synthetic)
Despite the “earthy” vibes of psychedelic therapy, ketamine is:
- 💯 Lab-made
- Originally synthesized in 1962 by Parke-Davis
- Used extensively in Vietnam for battlefield anesthesia
No mushrooms. No vines. Just chemistry.
9. Related Compounds and Cousins in the Chemical Family
Ketamine belongs to a family of arylcyclohexylamines that includes:
- Phencyclidine (PCP) – a more potent cousin
- Methoxetamine (MXE) – a research chemical
- Norketamine – an active metabolite
- Hydroxynorketamine (HNK) – may hold future promise as a safe antidepressant
Understanding these relationships helps scientists design better, safer medications.
10. FAQs: Rapid Fire Round!
Q: What is ketamine made of?
A: C₁₃H₁₆ClNO – carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and chlorine atoms arranged into a chiral molecule.
Q: Is ketamine natural or synthetic?
A: 100% synthetic. Created in labs via chemical synthesis.
Q: What is in ketamine nasal spray?
A: S-ketamine (esketamine) hydrochloride + stabilizers in a saline base.
Q: Is racemic ketamine the same as esketamine?
A: No. Racemic contains both R and S forms; esketamine is only the S form.
Q: Can you make ketamine at home?
A: Absolutely not. It requires high-level chemistry, safety measures, and is illegal to produce without a license.
11. The Future of Ketamine Compounding & Customization
Ketamine science is evolving rapidly. Look out for:
- Extended-release oral ketamine
- Enantiomer-specific formulas
- HNK-based antidepressants without dissociation
- Precision dosing based on genetic and metabolic profiling
12. Conclusion: Now You Know What Ketamine Is Made Of!
From atoms to anesthetics, now you’ve got a crystal-clear understanding of what ketamine is made of—and why that matters!
Whether you’re considering ketamine for treatment, curious about the science, or just love chemistry, this powerful little molecule has a lot packed into it. From its lab-based origin to its neurological impact, it’s truly a marvel of modern medicine.
So the next time someone drops “ketamine” into a conversation, you’ll be ready to explain not just what it does—but exactly what it’s made of.
Would you like a custom illustration or infographic to go along with this blog post? I can generate one on demand!